Ask me about:
- Science (biology, computation, statistics)
- Gaming (rhythm, rogue-like/lite, other generic 1-player games)
- Autism & related (I have diagnosis)
- Bad takes on philosophy
- Bad takes on US political systems & more US stuff
I'm not knowledgeable about most other things
Is there any point for current US-based "skilled immigrants" to stay in the US?
By "skilled immigrants" I mean people with advance degrees (PhD, MD, ...) holding all types of highly technical and managerial positions.
Asking this because skilled immigrants, at least in theory:
- knows, and has first-hand experience of how much bullshit one has to go through to immigrate,
- has enough bargaining power to move to another immigration-friendly country,
- let's just say that the upcoming US policies don't seem to be friendly to any immigrants at all...
But then US tech and research are supported largely by the same skilled immigrants. So I'm curious how that is supposed to play out...
Sorry this is a bit of a strange question.
P.S.: I'm... not asking for a friend. I've been constantly worried for the past two weeks; I try not to rush to conclusions, so the fact that I'm still worried concerns me. Double quotation marks because in the US it's literally the same government agency that manages all immigrants no matter how they got in the country (highly skilled worker, family of citizen, asylum, literally just crossed the border, ...)
Criss-cross void


Description: a black cat with its front legs stretched out and criss-crossed on top of each other.
Your friends shape your microbiome — and so do their friends
Analysis of nearly 2,000 people living in remote villages in Honduras reveals who’s spreading gut microorganisms to whom.
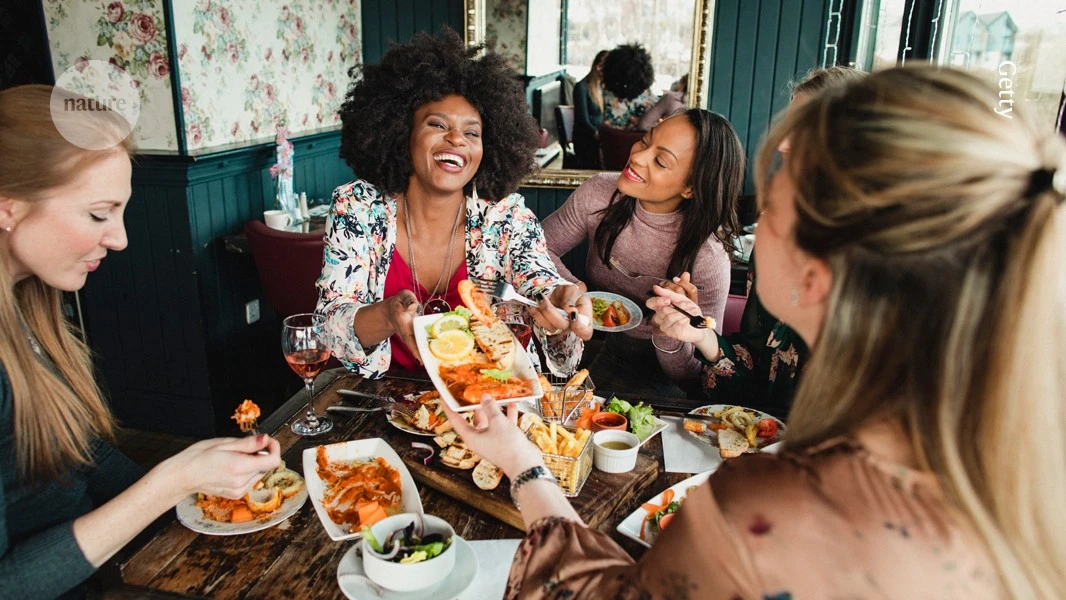

> A shared meal, a kiss on the cheek: these social acts bring people together — and bring their microbiomes together, too. The more people interact, the more similar the make-up of their gut microorganisms is, even if individuals don’t live in the same household, a study shows.
> The study also found that a person’s microbiome is shaped not only by their social contacts but also by the social contacts’ connections. The work is one of several studies that raise the possibility that health conditions can be shaped by the transmission of the microbiome between individuals, not just by diet and other environmental factors that affect gut flora.
What if we shared our microbiomes under the moonlight
Associated research article (open access): Beghini, F., Pullman, J., Alexander, M. et al. Gut microbiome strain-sharing within isolated village social networks. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08222-1
Another relevant research article cited by the news (also open access): Valles-Colomer, M., Blanco-Míguez, A., Manghi, P. et al. The person-to-person transmission landscape of the gut and oral microbiomes. Nature 614, 125–135 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05620-1
TIL of Darwin's Ark, a community research nonprofit aimed to better understand household pets (and they are actively seeking ppl to help with cat research!)
Join the world's largest pet citizen science project. Together, we can discover new ways to help pets and their people live happier, healthier lives.
The nonprofit's scientist co-founder was one of the organizers of a conference I attended, so that's how I learned! From their website:
> Darwin’s Ark was founded by two passionate pet lovers—a geneticist and an engineer—who noticed a glaring gap in scientific research. Many people had pets, but surprisingly little research focused on their health and wellbeing.
> This sparked the creation of Darwin’s Ark, a nonprofit organization that combines the perspectives of pet parents with the expertise of professional scientists to expand the scale and scope of pet research.
> Since then, Darwin’s Ark has helped thousands of pet owners contribute to the scientific understanding of their furry companions. We value pet owners’ insights—you know your animals best—and we believe in the transformative power of community science to drive discovery.
They just launched a new project, Darwin's Cats. And they are seeking out cat owners to submit data on their cats. I believe they also do genetic testing too and the data goes to researchers, instead of some shady startup company
My main social media app is Mastodon (technically Firefish which I will soon migrate to Iceshrimp... but those details are less relevant)
I consider Lemmy less so of a "social media" and more of a link aggregator/discussion forum... but yeah otherwise I try to use Lemmy a bit too. I still browse Reddit quite a lot, but only for individual communities that don't have equivalents on Lemmy, and I no longer post there
I never used much social media to begin with tbh... I feel pretty decent about the Fediverse. Despite all the drawbacks (blocklists, fedi drama, etc), I think people collectively managed to make an objectively better social media platforms compared to the previous corporation-dominated ones (at least by my personal metrics)
... which is why I never considered French press "inconvenient"... but from what I've heard from other coffee enthusiasts, they all found French press inconvenient precisely because they don't just pour the grounds down the drain & had to dispose it in the trash bin (and deal with the mess). Maybe I'm ill-informed somewhere, maybe something else... I'm not against just flushing the grounds though.
Currently live in a condo, I think every unit in the building came with one
The biggest advantage I could find is that they are insanely convenient for making French press coffee! French presses are otherwise a pain to clean (since there's no filter to aggegate the grounds), but having an in-sink disposal means I can just flush the coffee grounds directly into the sink. Besides this though I'm pretty indifferent to them
The code underlying the Nobel-prize-winning tool for modelling protein structures can now be downloaded by academics.

> AlphaFold3 is open at last. Six months after Google DeepMind controversially withheld code from a paper describing the protein-structure prediction model, scientists can now download the software code and use the artificial intelligence (AI) tool for non-commercial applications, the London-based company announced on 11 November.
When AlphaFold3 was first published the code wasn't publicly available (which is pretty bad for computational research), so this is good news that they finally released the code repository.
The GitHub repository: https://github.com/google-deepmind/alphafold3
Note that to request access one needs to sign a form & has to represent a non-commercial entity. If you receive access then allegedly you can easily run AlphaFold3 via docker
If you are allowed to shop online for one last time before being banned from online shopping for 3 years, would you buy/stock up on anything?
As the title goes... Per community rules, I'd appreciate it if we keep politics out of this discussion
So this is a bit counter to the news article's point, and apologies for linking to Reddit... but there has been a fairly hot post on the subreddit r/USCIS. A practicing immigration attorney was sharing some thoughts on how feasible the promises are https://www.reddit.com/r/USCIS/comments/1glflxy/so_what_now_an_immigration_attorney_perspective/. Some quotes:
IMO, no-- the economy makes way too much money from DACA folks. I do believe that they will dangle it like a carrot to appease right-wing voters. Major corporations employ DACAmented folks. The SSN from work permits have allowed more tax revenue to come in. Too much is at stake. Legally, the legal arguments at the courts surrounding DACA involve constitutional rights, which themselves aren't going anywhere anytime soon. It's honestly just a topic that is often talked about, but hardly understood by many.
I want to put this into perspective. There are 11 million undocumented immigrants in the US. Currently, DHS has about 92,000 officers, and ICE has about 21,000 officers. It is asinine to try to achieve this.
Let's say it actually does begin and people are getting rounded up. Guess what? Not all undocumented folks are just undocumented-- many have TPS, pending asylum applications, pending T/U Visas, and work permits (see my point regarding #1). Unless a migrant has an expedited removal (not likely), DHS/ICE still needs to process each deportee, assign them A#s, and follow basic procedures. If they don't? That's a very easy way to reverse a deportation order. It's the equivalent of convicting someone of murder using a confession made under a very obvious 4/5th amendment violation. Slam dunk case.
Oh, and you know who has to handle all of these deportation cases? Federal DHS attorneys. They're already overworked, and they tend to exercise discretion. If no discretion, the overworked ones tend to gloss over cases and provide weak arguments. Only major attention is paid to serious crimes. You'd be surprised the amount of times DHS attorneys have gotten my clients' names wrong or made procedurally embarrassing typos.
... assuming the administration still follows basic social contracts, that is. If the Trump administration actually uses the military to forcefully enforce mass deportations, then I feel the US is going to be fucked on so many different more levels... and there would be way more to worry than just the deportations
Well neuroscience isn't a very old field... More seriously though, I think biomedical scientists know surprisingly little about something if NIH doesn't fund it... aaand that's how we understood so little about our own household companions (and a bit too much about cancer. Seriously why do we know so many weird things about cancer much of those don't even translate into therapeutics)
Why do wet dogs shake themselves dry? Neuroscience has an answer
Deciphering how mammals respond to sensations through their fur could inspire further research on skin sensitivity.
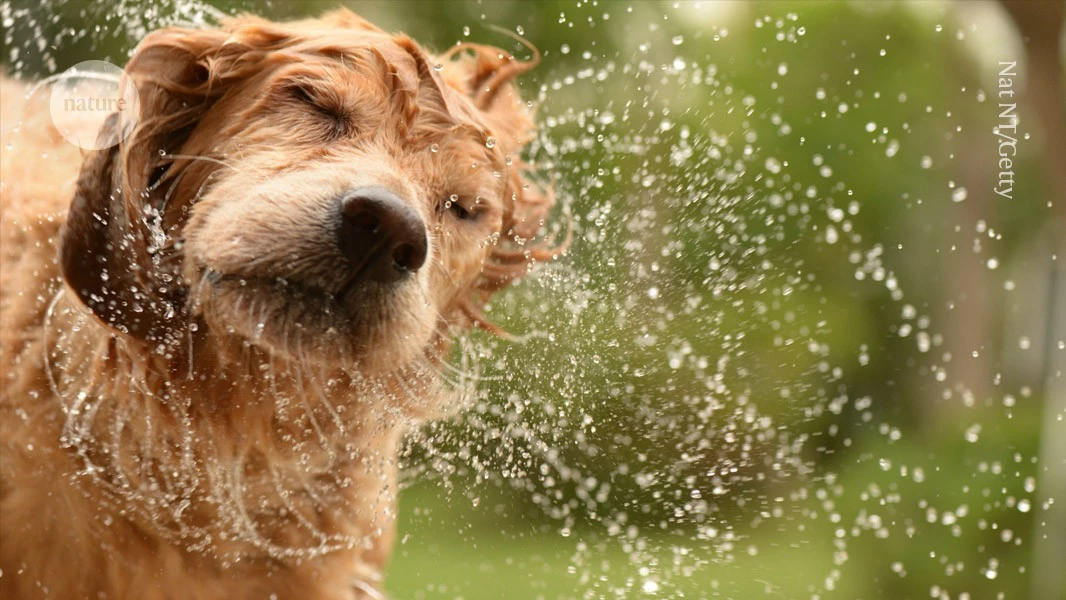

> When a dog shakes water off its fur, the action is not just a random flurry of movements — nor a deliberate effort to drench anyone standing nearby.
> This instinctive reflex is shared by many furry mammals including mice, cats, squirrels, lions, tigers and bears. The move helps animals to remove water, insects or other irritants from hard-to-reach places. But underlying the shakes is a complex — and previously mysterious — neurological mechanism.
> Now, researchers have identified the neural circuit that triggers characteristic ‘wet dog’ shaking behaviour in mice — which involves a specific class of touch receptors, and neurons that connect the spinal cord to the brain. Their findings were published in Science on 7 November.
> “The touch system is so complex and rich that [it] can distinguish a water droplet from a crawling insect from the gentle touch of a loved one,” says Kara Marshall, a neuroscientist at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas. “It’s really remarkable to be able to link a very specific subset of touch receptors to this familiar and understandable behaviour.”
Research article was featured on the cover of this issue of Science, with a glorious picture of a brown bear doing the "wet dog shake" (https://www.science.org/toc/science/current)
Research article: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adq8834
Please let me know if there is paywall
Disease: /LOSS


Brought to you by PubTator 3.0: an AI-powered literature resource for unlocking biomedical knowledge
(This is actually tooth loss but it was annotated as "/LOSS" in the data. Also this is not a paper on tooth loss)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/pubtator3/publication/30090999?text=@DISEASE_Tooth_Loss
I... think this question is a bit more complicated for this community. Following are only my personal opinion
Prescribed medication? I think so, I'd rather be physically and mentally healthy rather than have the other alternative. And usually medication (even ones with noted negative effects) are meant do do more good than harm so...
Recreational drugs... the line between this and the above is surprisingly not as clear-cut as it seems. I believe there are active lines of study of using various psychedelic compounds to treat mental disorders or other conditions... Personally I would take medically prescribed psychedelics if I am 1) under medical supervision and 2) based on evidence it would help my mental health (maybe that's the answer to the question?)
Hard drugs: I don't see how they can make anyone a better person, and no
Reminds me of this post of the same community: https://lemmy.world/post/4492190
Probably in K-12? Like seriously everyone in my "friend" groups and half of my classes knew something about me was off, and I believe I was known as the eccentric genius throughout middle/high school (and my HS had a lot of smart students). But the broader culture I was in didn't believe in mental health so...
Other than that... there were two people I relate to very well on Mastodon (when I first joined), one of whom is very openly autistic; hence why I got tested. That's probably as obvious as it gets
Not great... I'm not a US citizen yet so voting isn't possible. Only thing I could do is vote with my feet... so I moved out of Texas for good earlier this year. I think my current location is as safe as it gets in regards to avoiding political violence (since I'm not exactly in a group that the right isn't threatening) so there's that
Other than that? Nothing... If the worst happens I'll just hole-up in the building and ask my boss for permission to work from home
I looked at their individual page (https://www.darkpattern.games/pattern/4/psychological-dark-patterns.html)...
If deleting the game and starting over from scratch sounds like a horrible idea and a waste of your investment, then the game has Endowed Value for you. The more time and money that you invest in the game, the more value it has over a fresh copy of the game.
So I guess they are referring to is something more transactional... for example, if I spent $100 on a gacha game or loot boxes to get a bunch of ultra-rare SSRs. I'd be pretty compelled to keep playing since I've already spent so much money on it.
They are not counting, for example, that I get hooked on some weird roguelike game because I genuinely want to get better at it but can stop any time. And if I lose my save file I would still happily start from scratch again (which, hilariously, a pattern named Infinite Treadmill is marked for both Slay the Spire and Balatro... https://www.darkpattern.games/pattern/14/infinite-treadmill.html)
I clearly didn't drink enough coffee for this before posting
My bad, the original news article did a good job at explaining the missing link... I misunderstood what you were asking
- C-section babies seem to have more immune system-related diseases (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.07.040), so scientists think they would benefit from special treatment
- Scientists tried to fix this by giving the babies vagina-derived bacteria (https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4039); couldn't find any more reports on this but it seems like these don't work super well?
- This is a proof-of-concept by the lab highlighted in the news (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.047), they tried using fecal matter and it worked
- The abstract featured in the news is now a clinical trial that is in progress
I think that's pretty much it
This is the study they were referring to: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.07.040
C-section babies have slightly higher risks of several diseases related to immune system function, and the hypothesis is that it is because these babies have slightly less developed immune systems
Giving faecal transplants to children born by caesarian section is promising, early clinical trial results show.
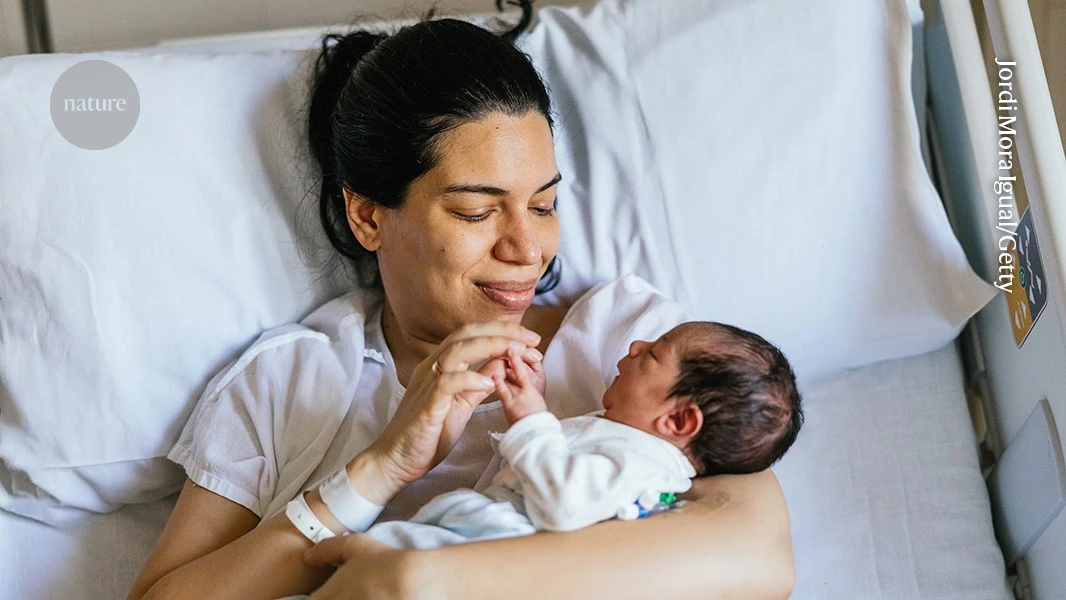

> Feeding a baby born by caesarean section milk containing a tiny bit of their mother’s poo introduces beneficial microbes to their gut, according to a clinical trial. The approach might one day help to prevent diseases during childhood and later in life.
> Some studies show that babies born by c-section, rather than vaginal birth, have a higher risk of asthma, inflammation of the digestive system and other diseases associated with a dysfunctional immune system... Experiments have attempted to compensate for that by swabbing babies born by c-section with microbes from their mother’s vagina or giving them these microbes orally, a practice known as ‘vaginal seeding’. But this technique has had limited success, because vaginal microbes, scientists have learnt, cannot effectively colonize infants’ guts...
> Helve and his colleagues have been pioneers in testing whether faecal transplants can instead improve the health of a baby’s microbiome. In their latest trial, which recruited women scheduled for a c-section at the Helsinki University Hospital, the researchers mixed a fluid containing 3.5 milligrams of a mother’s poo into milk and gave the concoction to the corresponding baby. They did this for 15 babies during their first feed. Another 16 babies received a placebo.
> An important next step in the field, Shao says, would be to pinpoint the specific maternal gut microbes that are most likely to transmit to and colonize their babies’ guts. Shao asks: “If these species do exist across human populations, wouldn’t it be more effective and safer” to give newborns a laboratory-made transplant that’s guaranteed to be pathogen-free?
"This is the shit"
But seriously don't try this at home. Fecal matters can contain pathogens, in fact 54 of the 90 women screened were excluded because of detected pathogens. If this goes well maybe ppl can make some type of lab-made probiotics for C-section babies or stuff
The abstract presented at IDWeek 2024: https://idweek2024.eventscribe.net/index.asp?presTarget=2886841
Knowing the genes responsible for water bears’ radiation tolerance could lead to diverse applications, from cancer treatment to space exploration.
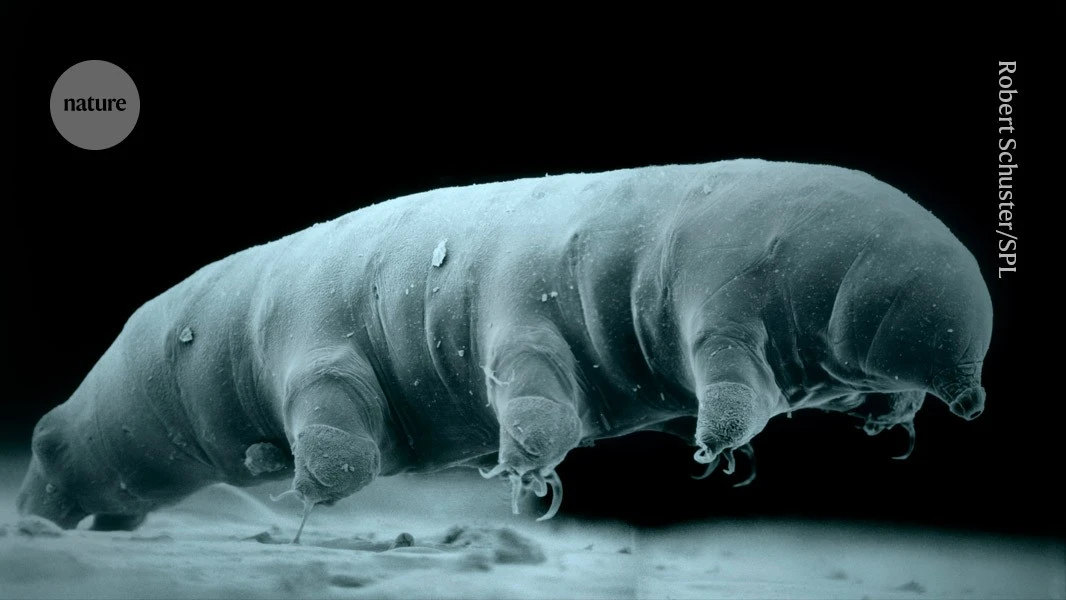
> A newly described species of tardigrade is giving scientists insights into what makes these tiny eight-legged creatures so resistant to radiation.
> Now, scientists have sequenced the genome of a species new to science, and revealed some of the molecular mechanisms that give tardigrades their extraordinary resilience. Their study, published in Science on 24 October, identifies thousands of tardigrade genes that become more active when exposed to radiation. These processes point to a sophisticated defence system that involves protecting DNA from the damage that radiation causes and repairing any breaks that do occur.
> The authors hope that their insights could be harnessed to help protect astronauts from radiation during space missions, clean up nuclear pollution or improve cancer treatment.
"Radiation and multi-omics sequencing go brrrr"
Original paper on Science: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adl0799
AI watermarking must be watertight to be effective (on SynthID, DeepMind's "watermarking" tool for detecting LLM outputs)
Scientists are closing in on a tool that can reliably identify AI-generated text without affecting the user’s experience. But the technology’s robustness remains a challenge.

> The ability of large language models (LLMs) to create text and images almost indistinguishable from those created by humans is disrupting, if not revolutionizing, countless fields of human activity. Yet the potential for misuse is already manifest, from academic plagiarism to the mass generation of misinformation.
> This week, Sumanth Dathathri at DeepMind, Google’s AI research lab in London, and his colleagues report their test of a new approach to ‘watermarking’ AI-generated text by embedding a ‘statistical signature’, a form of digital identifier, that can be used to certify the text’s origin. The word watermark comes from the era of paper and print, and describes a variation in paper thickness, not usually immediately obvious to the naked eye, that does not change the printed text. A watermark in digitally generated text or images should be similarly invisible to the user — but immediately evident to specialized software.
> Dathathri and his colleagues’ work represents an important milestone for digital-text watermarking. But there is still some way to go before companies and regulators will be able to confidently state whether a piece of text is the product of a human or a machine. Given the imperatives to reduce harm from AI, more researchers need to step up to ensure that watermarking technology fulfils its promise.
This is the official paper and the Nature News report related to the SynthID project. Basically, "watermarking" to make sure the model outputs can be easily recognized computationally... but it's not foolproof. Especially relevant in light of AI regulations. News article itself contains some interesting opinions
Paper: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08025-4
GitHub repo: https://github.com/google-deepmind/synthid-text
I happen to know a few folks who work in this field (detecting fraudulent scientific papers). This is a bit of an insider knowledge, but there are science sleuths who are fearing for their lives... there might be some seriously shady stuff going on behind research paper mills, but I don't know who will be the one digging those up.
If it is just on an individual level though methinks Retraction Watch does a decently good job at informing what might or might not be trustworthy
A recent report on Retraction Watch, a PhD student was trying to figure out who's behind a papermill: https://retractionwatch.com/2024/10/01/hidden-hydras-uncovering-the-massive-footprint-of-one-paper-mills-operations/
This is from Nature News today: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-03427-w. Heard a bit about this startup even before so...
Me personally? No... I haven't been celebrating much of anything at all for the past several years, not even Thanksgiving/Christmas/other ethnic holidays. Depression & lack of friends have been rough... and the area I live in now is mostly consisted of high-end restaurants, so I don't anticipate getting a discount for costume either
However the building I moved in seems to do lots of events, including an annual trick-or-treat for kids in the building! I'm kind of curious what the kids in the building will be up to, there is a sizable number of people in the building who have children so there's that
Jokes on me, my cats can somehow recognize me from the sound of me walking up to the front door (and only me, not when anyone else is visiting)... No idea if anything can make them not recognize me
Tommy trying to look like a seal today


Image description: a black cat lying down on a ledge next to a window. Only one of the hind legs is visible on the cat.
This again??
This time once archive.org is back online again... is it possible to get torrents of some of their popular data storage? For example I wouldn't imagine their catalog of books with expired copyright to be very big. Would love a community way to keep the data alive if something even worse happens in the future (and their track record isn't looking good now)
Pretty sure the "intimate detail" is just the editor being horny... I didn't make the title don't blame me
Hehe
Blame the Nature News editor for this, the paper title wasn't horny at all
Three sperm proteins work together as matchmakers to enable fertilisation in vertebrates.
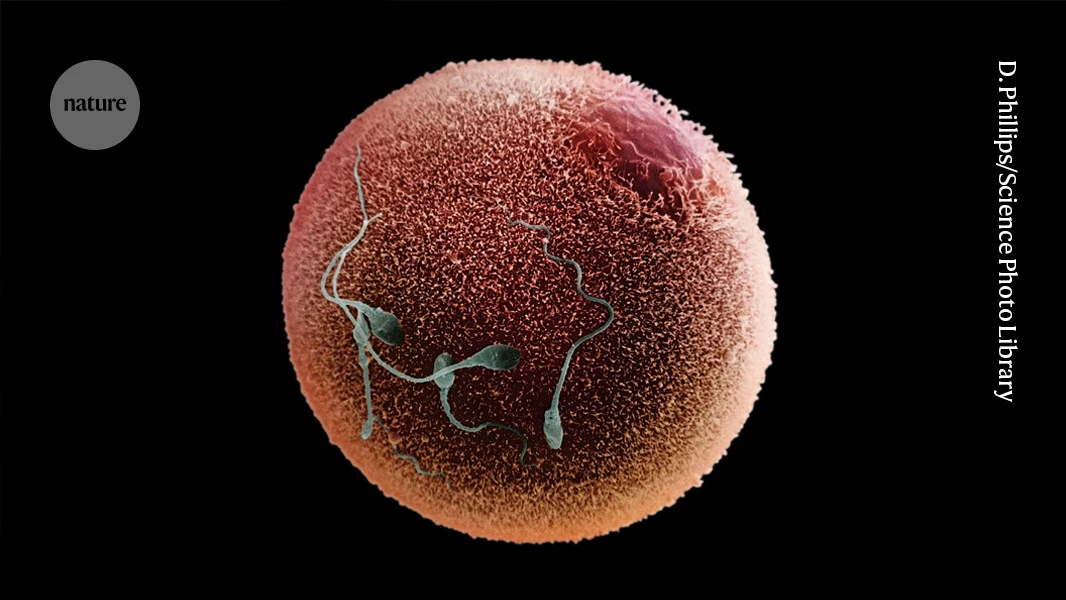
> AlphaFold predicted that three sperm proteins work together to form a complex. Two of these proteins were previously known to be important for fertility. Pauli and her colleagues then confirmed that the third is also critical for fertility in both zebrafish and mice, and that the three proteins interact with one another.
> The team also found that, in zebrafish, the trio creates a place for an egg protein to bind, providing a mechanism by which the two cells could recognize one another. “It’s a way to say, ‘Sperm, you found an egg’ and ‘Egg, you found a sperm’,” says Andreas Blaha, a biochemist at the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology and co-author of the paper.
> The findings might one day yield a way to screen people struggling with infertility, to find out whether problems with this complex could be the cause, says Wright.
> And the results highlight a role for AlphaFold in studying fertilisation, he adds. “We’re limited in terms of experiments,” he says. “It might be that these modelling studies have an important role to play in the future.”
In other words, the team used AlphaFold to help with discovering a three-protein complex that allows sperm & egg to bind together. And this complex seems to be conserved between zebrafish and humans (!!). Despite the news title: this study is actually less about AlphaFold and more about using it to help do very important biochemistry
Original paper (open access): A conserved fertilization complex bridges sperm and egg in vertebrates. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.09.035
In animals, the molecule automatically reduced blood-sugar levels without causing them to dip too much.
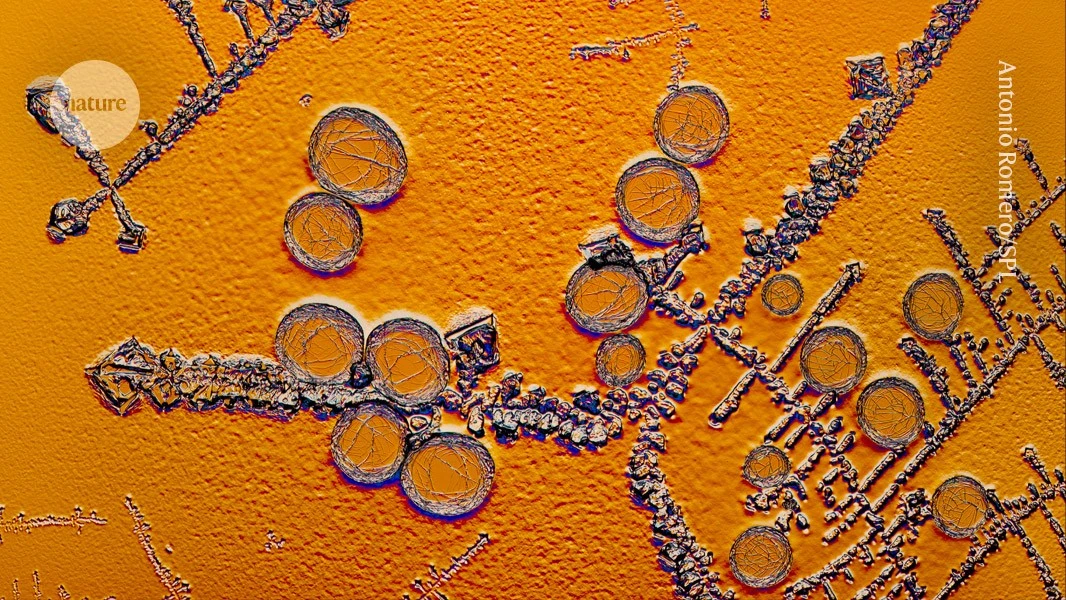

"Scientists have designed a new form of insulin that can automatically switch itself on and off depending on glucose levels in the blood. In animals, this ‘smart’ insulin reduced high blood-sugar concentrations effectively while preventing levels from dropping too low... A spokesperson for Novo Nordisk says that although this study is a proof of principle of NNC2215’s glucose-sensitive insulin properties, further research to optimize the molecule is ongoing."
From the research article: "Here we report the design and properties of NNC2215, an insulin conjugate with bioactivity that is reversibly responsive to a glucose range relevant for diabetes, as demonstrated in vitro and in vivo... In animal studies, the glucose-sensitive bioactivity of NNC2215 was demonstrated to lead to protection against hypoglycaemia while partially covering glucose excursions."
Brought to you by a passionate research group from Novo Nordisk, home of the $1,349 per month weight-loss drug Wegovy
This is still fairly early-stage research so the final commercialization might take quite some time
The article itself, open access: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08042-3
Had a fairly important work deadline that was supposed to be end of this month. Unfortunately, I didn't read institutional policies carefully enough, and institutional fuckery mandates that they receive all the documents one week prior. So my actual deadline is like next Monday
So yeah, I'll be working this entire weekend... at least the good news is I can probably get two free days off by the end of this month (which I wanted to do anyway)
I am not joking; the only thing I can imagine is for some bizarre reason a bowling ball noise followed by a comical noise of striking pins. I know there is a person but I couldn't imagine that person
This is a thought experiment "Ball on a Table" for detecting whether someone has Aphantasia. What do you see when you perform this experiment?
This is more of me trying to understand how people imagine things, as I almost certainly have Aphantasia and didn't realize until recently... If this is against community rules, please do let me know.
The original thought experiment was from the Aphantasia subreddit. Link: https://www.reddit.com/r/Aphantasia/comments/g1e6bl/ball_on_a_table_visualization_experiment_2/
Thought experiment begins below. --- Try this: Visualise (picture, imagine, whatever you want to call it) a ball on a table. Now imagine someone walks up to the table, and gives the ball a push. What happens to the ball?
Once you're done with the above, click to review the test questions:
- What color was the ball?
- What gender was the person that pushed the ball?
- What did they look like?
- What size is the ball? Like a marble, or a baseball, or a basketball, or something else?
- What about the table, what shape was it? What is it made of?
And now the important question: Did you already know, or did you have to choose a color/gender/size, etc. after being asked these questions? ___
World’s oldest known (representational) artwork in Indonesian cave dated using lasers
A cave painting on a southeast Asian island is estimated to be at least 51,200 years old.
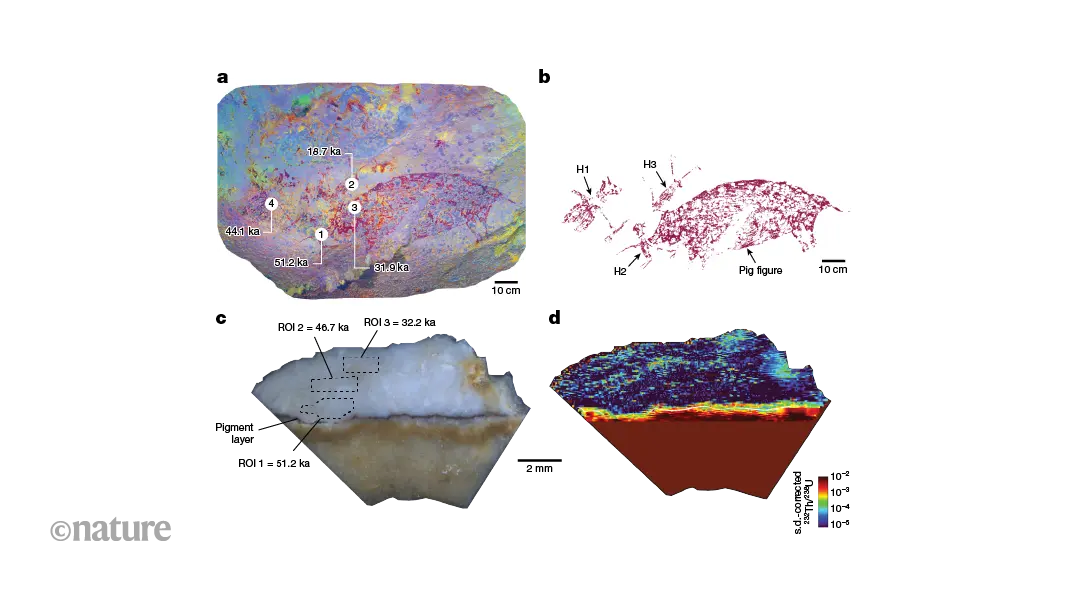
Laser-induced imaging of radioactive elements was used to work out the age of an ancient cave painting on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi. The results reveal that the narrative scene is 51,200 years old, making it the earliest known example of representational art. This study challenges previous dating methods and suggests a deeper origin for human image-making and storytelling.
TL;DR or if you don't have access to the article: the researchers invented a faster, less-destructive and more-accurate rock art dating method & applied it to humanity's oldest known rock art in Sulawesi, Indonesia. The art is at least 51,200 years old (authors' lower estimate)!
Edit: contrary to what the news title original stated: this is the oldest representational art, not the literal oldest human-created art.
The paper itself (open access): https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07541-7
The internet archive may have just suffered a security breach
Per their error message, "See 31 million of you on HIBP!"
If anyone can provide a slightly more up-to-date souce (their X post, for example) I'd appreciate it
Hacker News post: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=41792500
Complete (telomere-to-telomere diploid genome) sequencing of genomes of six ape species
The Telomere-to-telomere consortium's primate project. We now have complete, diploid genomes of six ape species (chimpanzee, bonobo, gorilla, Bornean orangutan, Sumatran orangutan, and siamang). Maybe this will show up on Nature or somewhere next year :D
Manuscript is literally just out on biorxiv.org past Saturday... So title/details subject to change, and unfortunately there are no fancy news articles making it any easier to read
Links:
Double standards in promotion and tenure (for underrepresented minority faculty: especially if you are a women of colour)
Despite much anecdotal evidence, few studies show pervasive racial bias in promotion and tenure decisions. By analysing 1,571 real promotion and tenure cases across five US universities, Masters-Waage et al. find double standards negatively applied to scholars of colour, and especially women of colo...
Despite much anecdotal evidence, few studies show pervasive racial bias in promotion and tenure decisions. By analysing 1,571 real promotion and tenure cases across five US universities, Masters-Waage et al. find double standards negatively applied to scholars of colour, and especially women of colour, even after accounting for scholarly productivity.
Shortcoming of this paper is that it is
- 1500+ individuals from five typical research-intensive US-based institutions, so other countries/types of institutions might see differences. Two HBCUs were also excluded, wouldn't be surprised if they see less racism.
- I believe it was mentioned somewhere that the team only looked at Black and Hispanic faculty members, because other minorities are too few in numbers to look at... If you are wondering, Asians/Asian Americans are not considered minorities in academia.
Original paper, open access & quite easy to read if you are interested
- https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-024-01977-7
Dataset:
- https://osf.io/9xu65/?view_only=8af03fe8158c43a185ce807a17e43431
The associated Science News articles, both original URL and archive.org ver:
- https://www.science.org/content/article/racial-bias-can-taint-academic-tenure-process-one-particular-point
- https://web.archive.org/web/20241005023358/https://www.science.org/content/article/racial-bias-can-taint-academic-tenure-process-one-particular-point
